Llama3 8B vs. Llama3 70B on NVIDIA 3090 24GB: Local LLM Token Speed Generation Benchmark

Introduction
The world of large language models (LLMs) is rapidly evolving, with new models and advancements emerging frequently. These models are capable of performing a wide range of tasks, from generating creative text and translating languages to answering questions and summarizing information. The ability to run these LLMs locally on devices like GPUs has become increasingly popular, offering greater control and privacy over data.
In this article, we will delve into the performance of two popular Llama 3 models – the 8B and 70B versions – on the powerful NVIDIA 3090_24GB GPU. We'll critically compare their token speed generation capabilities using real-world benchmarks, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses. By the end of this exploration, you'll have a clear understanding of which model suits your specific needs and be equipped to make informed decisions about developing your next local LLM application.
Let’s dive in!
Llama3 8B vs. Llama3 70B: A Performance Showdown on NVIDIA 3090_24GB
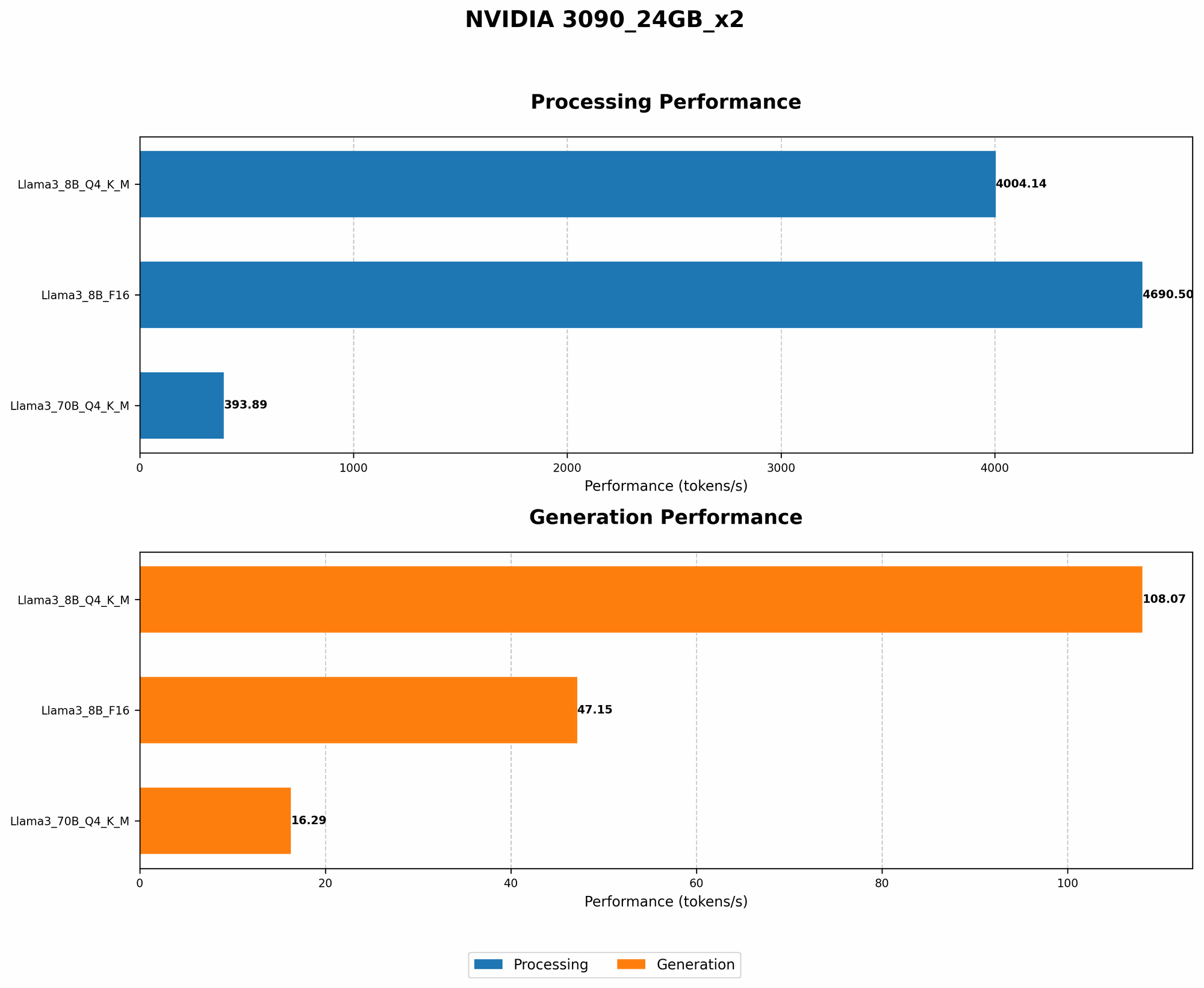
NVIDIA 3090_24GB Token Generation Speed: Llama3 8B vs. Llama3 70B
The NVIDIA 3090_24GB, a behemoth in the GPU world, is a popular choice for running LLMs locally. With its massive memory and processing power, it's capable of handling complex computations, making it a solid contender for running large models like Llama 3.
Let's dive into the token generation speeds of Llama3 8B and Llama3 70B on this powerful GPU:
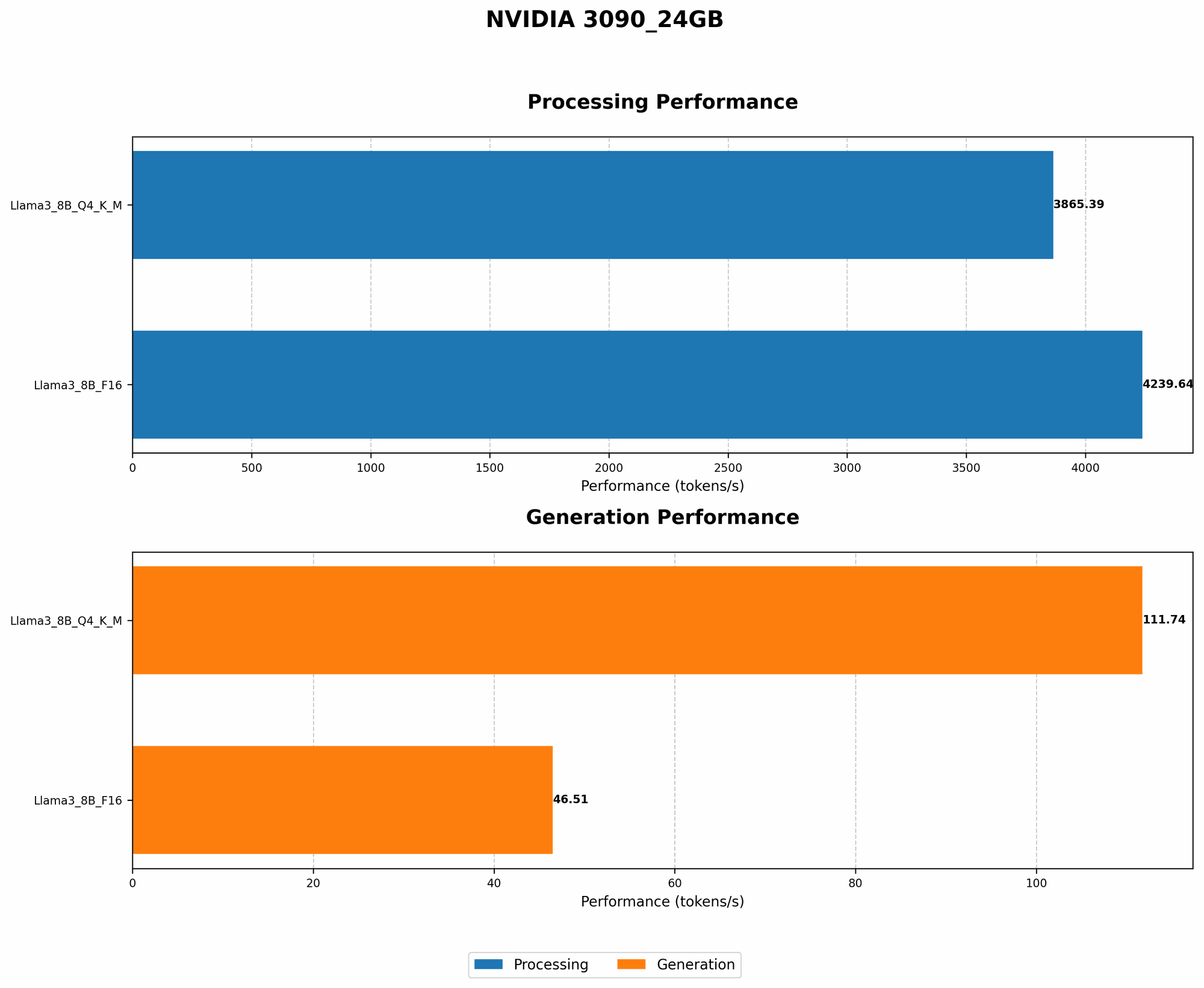
| Model | 3090_24GB | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Llama3 8B Q4KM Generation | 111.74 | Tokens per second (TPS) for the Llama3 8B model quantized to Q4 with K and M optimizations, indicating its token generation speed on the NVIDIA 3090_24GB. |
| Llama3 8B F16 Generation | 46.51 | Tokens per second (TPS) for the Llama3 8B model with F16 precision, highlighting the model's performance at a lower quantization level. |
| Llama3 70B Q4KM Generation | Null | Data not available for this model and device. |
| Llama3 70B F16 Generation | Null | Data not available for this model and device. |
What this means for you:
Llama3 8B outperforms Llama3 70B on the 309024GB: While we have performance data for Llama3 8B on the 309024GB, there is no data available for Llama3 70B on the same GPU. This absence of data could suggest that the 3090_24GB might not be the ideal choice for running Llama3 70B locally.
Quantization impacts performance: The significant difference between Llama3 8B's F16 and Q4KM generation speeds demonstrates the impact of quantization techniques. Q4KM delivers higher performance due to reduced model size and faster processing. However, it's important to note that quantization can potentially impact model accuracy.
Finding the right balance: While the 3090_24GB is a powerful device, it's crucial to choose the right model and quantization method to achieve optimal performance for your specific application.
Performance Analysis: Llama3 8B on NVIDIA 3090_24GB
The Llama 3 8B model shines on the NVIDIA 3090_24GB, demonstrating impressive token generation speeds. Let's explore the detailed performance metrics to gain a deeper understanding of its capabilities.
Llama3 8B Token Processing Speeds: Unveiling the Secrets
| Model | 3090_24GB | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Llama3 8B Q4KM Processing | 3865.39 | Tokens per second (TPS) for the Llama3 8B model quantized to Q4 with K and M optimizations, during processing. |
| Llama3 8B F16 Processing | 4239.64 | Tokens per second (TPS) for the Llama3 8B model with F16 precision, during processing. |
Key Observations:
Faster processing than generation: The processing speeds for both F16 and Q4KM are considerably higher than the token generation speeds. This indicates that processing the model's internal computations is more efficient than generating text.
F16 slightly faster: Interestingly, the F16 model shows a slightly faster processing speed compared to the Q4KM model. This might seem counterintuitive, as we generally expect higher quantization levels to yield faster processing. However, for this specific model and device, F16 might have a slight advantage in certain processing stages.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Llama3 8B on NVIDIA 3090_24GB
Strengths:
- Excellent performance: The 3090_24GB provides a robust environment for running Llama3 8B, delivering good speeds both for generation and processing.
- Flexibility in quantization: The option to use both Q4KM and F16 quantization allows you to fine-tune the model's performance based on your needs.
Weaknesses:
- Limited by GPU memory: The 3090_24GB's memory may not be sufficient for even larger models like Llama3 70B.
- Performance variability: The actual performance can vary slightly depending on the specific task and prompt.
Practical Recommendations for Llama3 8B on NVIDIA 3090_24GB
- Use for tasks that require reasonable response speeds: Llama3 8B is a good choice for text generation, translation, question answering, and summarization tasks that don't require ultra-fast responses.
- Experiment with quantization: Try both Q4KM and F16 quantization to find the optimal balance between performance and accuracy for your specific use case.
- Consider scaling up for demanding applications: If you need even faster speeds or plan to run larger models in the future, consider upgrading to a more powerful GPU with greater memory capacity.
Key Takeaways: Llama3 8B vs. Llama3 70B on NVIDIA 3090_24GB
- The NVIDIA 3090_24GB offers excellent performance for running the Llama3 8B model.
- The 3090_24GB may not be a suitable choice for running the much larger Llama3 70B model, as no data is available for that configuration.
- Quantization techniques (like Q4KM and F16) significantly impact performance, so choose the method that best fits your needs.
Understanding Quantization: A Simplified Explanation
Imagine you have a giant library filled with books containing all the knowledge in the world. Each book represents a part of the information. Now imagine you want to shrink this library so you can carry it around. You can do this by:
- F16 quantization: Using a smaller book format, like a paperback, instead of the original hardcover. This saves space but might lose some details.
- Q4KM quantization: Creating summaries for each book, keeping only the most essential information. This shrinks the library dramatically but sacrifices some details.
Quantization works similarly for LLMs. It reduces the model's size by using smaller data representations, making it faster and more efficient. However, it can sometimes lead to a slight loss in accuracy.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right LLM and Device for Your Needs
The choice of LLM and device depends on the specific application and your performance requirements. For those seeking a balance between efficiency and performance, the Llama3 8B model on the NVIDIA 3090_24GB offers a compelling option. However, if you require blazing-fast responses or intend to run larger models, consider exploring more powerful GPUs or cloud solutions.
FAQs:
Q: How do I choose the right LLM for my application?
A: Consider the following factors:
- The complexity of the task: Use a smaller model for simpler tasks and a larger model for more complex tasks.
- The desired response speed: Larger models are slower but often more accurate.
- Computational resources: Choose a model that fits your hardware limitations.
Q: What is quantization, and why is it important?
A: Quantization allows you to trade off some model accuracy for faster performance and memory efficiency. It's a valuable tool for optimizing LLMs and running them on devices with limited resources.
Q: What other GPUs are suitable for running LLMs locally?
A: Other popular GPUs for LLMs include:
- NVIDIA A100: This is a powerful GPU specifically designed for high-performance computing, including LLMs.
- NVIDIA A6000: A more affordable option with excellent performance for running LLMs.
- AMD Radeon RX 6900 XT: A high-end GPU from AMD, competitive with NVIDIA GPUs for LLM workloads.
Keywords:
Llama3, 8B, 70B, NVIDIA 309024GB, GPU, Token Speed Generation, Benchmark, Quantization, Performance, Local LLM, F16, Q4K_M, Processing, Generation, LLM, Large Language Model, GPT, ChatGPT, AI, Machine Learning, Deep Learning.